TL;DR
- All Hyperscale cloud providers have tools to provide carbon emission analysis of services running in their cloud
- The Cloud Carbon Footprint Tool is a good starting point for organisations wishing to analyse cloud and on-premises carbon emissions
- Measuring cloud carbon emissions is part of the wider Stage 3 emissions measurement of your organisation – e.g. Business Travel, Commuting, Commercial Buildings
Why Measure Emissions?
In 2001, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol sought to categorize corporate greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) – using three buckets, named: scope 1, scope 2, and scope 3. To better understand this emission classification system, you can use the 3 B’s acronym burn, buy, and beyond. (see: Green Business Bureau)
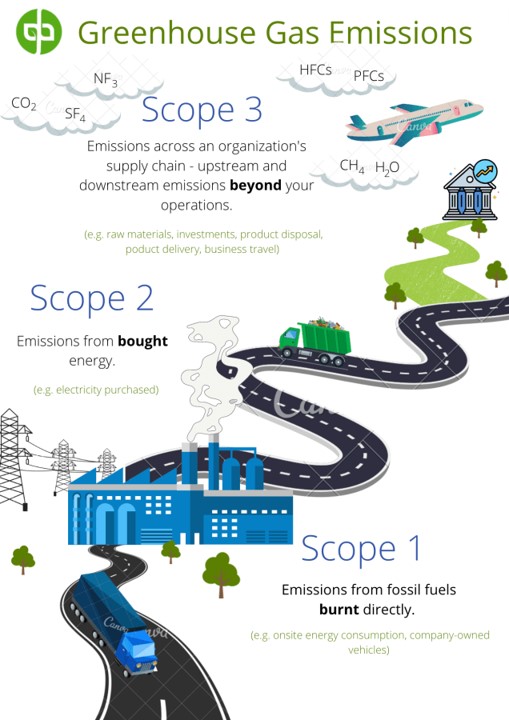
Scope 3 emissions account for ~70% of an organization’s carbon footprint.
How to Measure Cloud Provider Missions
- Cloud Provider emissions fall under scope 3
- The Greenhouse Gas Protocol provides calculation guidance for Stage 3, which was first released in 2011, but this doesn’t include guidance on cloud provider emission calculations*
- Microsoft was the first Hyperscale cloud provide to offer a tool that provided insights into the emissions from running resources in their cloud
- History highlights
- January 2020 – Microsoft Sustainability Calculator
- March 2021 – Thoughtworks Open Source Cloud Carbon Footprint tool
- October 2021 – Google Cloud Carbon Footprint
- March 2022 – AWS Carbon Footprint Tool
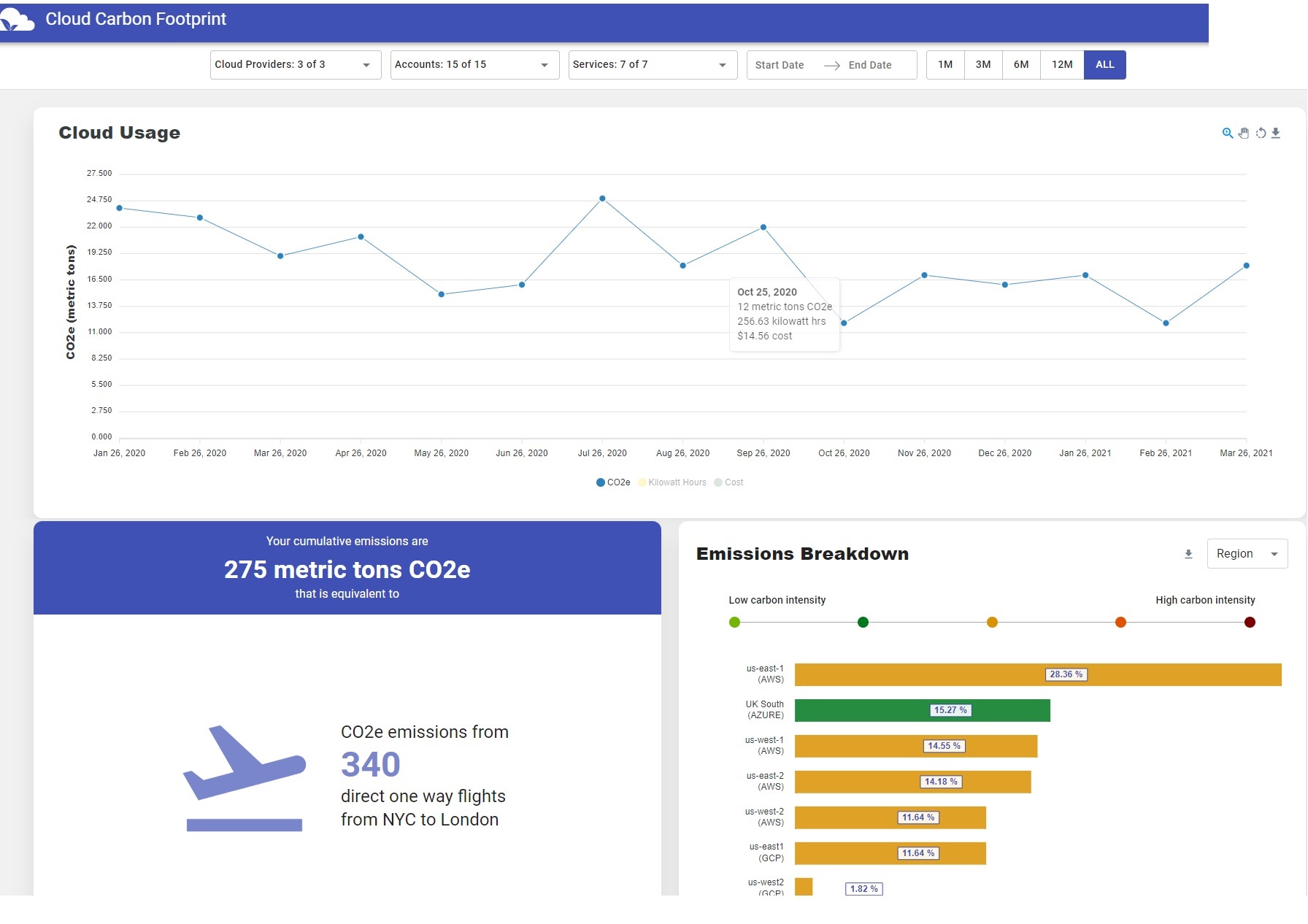
- The Thoughtworks Open Source Cloud Carbon Footprint tool allows consolidated reporting from Azure, Google and AWS.
Open Source Cloud Carbon Footprint Tool
- A demo version is available here: https://demo.cloudcarbonfootprint.org/
- You can run a version locally
- https://www.cloudcarbonfootprint.org/docs/getting-started
- Will inherit core estimation logic
- Run with mocked data: https://www.cloudcarbonfootprint.org/docs/run-with-mocked-data
- You can also fork repository to provide greater flexibility over customising calculation logic and contribute to the core project
- You can also use the tool for on-premises estimation for compute and storage
Beyond Cloud
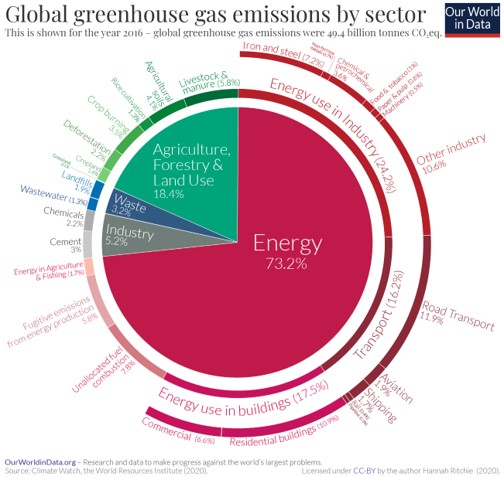
- Global greenhouse gas emissions from the tech sector are on par or larger than the aviation industry, at around 3% for ICT and 2% for aviation respectively*
- Measuring cloud carbon emissions is part of the wider Stage 3 emissions measurement of your organisation – e.g. Business Travel, Commuting, Commercial Buildings
- Reducing carbon emissions in all areas is important
Published: August 2022

